Dacryocystitis is an infection of the tear sac (called lacrimal sac) that sometimes leads to pus formation. The infection may be caused due to blockage of the nasolacrimal duct, which starts from the tear sac (in which tears drain) into the nose.
Causes of Dacryocystitis
It is most commonly caused by bacterial. Very rarely, it may also be due to a “stone” in the tear duct.
In congenital forms the drainage system near the lacrimal sac is either not fully developed, obstructed or stenosed (abnormally narrowed).
Signs & Symptoms
Dacryocystitis may occur suddenly (acute) or may be longstanding (chronic).
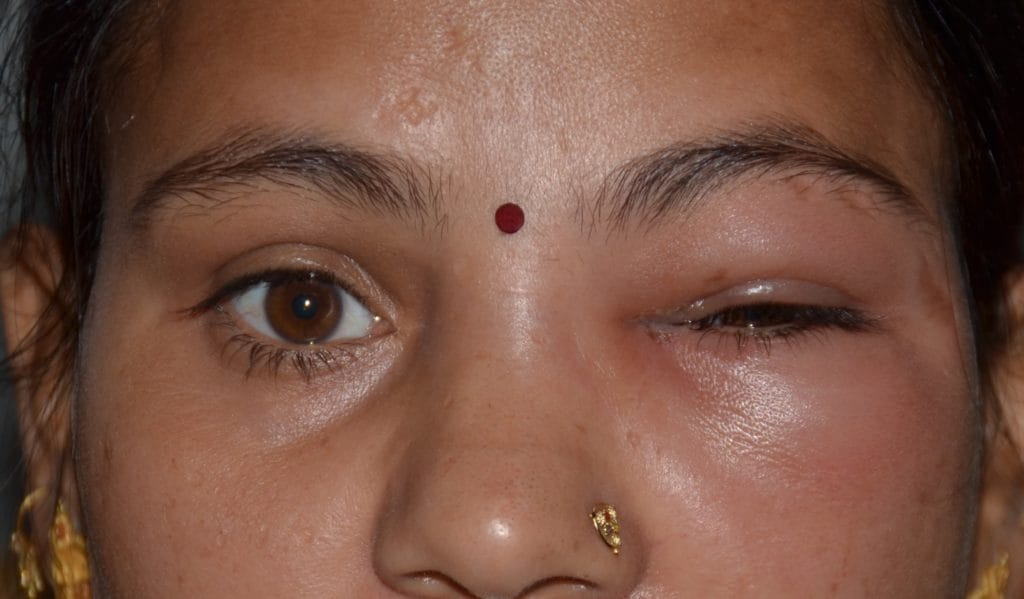
In acute infection, the area around the tear sac is painful, red and swollen. The area around the eye may also become red and watery and may ooze pus. Sometimes, when slight pressure is applied to the tear sac, it may even push thick material through the opening at the inner corner of the eyelid near the nose, called punctum.
Often the infection in acute dacryocystitis is mild. But, sometimes the infection is severe and can cause fever. More serious condition of acute dacryocystitis include extension into the orbit (cavity or socket of the skull in which the eye and its attachments are situated). This leads to formation of pus and development of orbital cellulitis (inflammation of eye tissues behind the orbit). This condition may lead to blindness and, rarely, even death.
In chronic dacryocystitis, there may be a discharge from the eye. Tearing (obstruction of the outflow of tears, debris and epithelial cells from the surface of the eye) is the most common presentation.
Since, the tears are full of bacteria, it can even cause conjunctivitis that may lead to redness and watering in the eyes.
How is dacryocystitis diagnosed?
Diagnosis is made based on signs & symptoms. When pressure over the lacrimal sac causes release of pus. However, sometimes, special x-rays are used to help find a cause for the blockage or narrowing in the tear duct.
Treatment
An acute dacryocystitis is usually treated with oral antibiotics taken by mouth. Warm compresses with gentle massage, several times a day, at the affected area also helps.
The definitve treatment of chronic dacryocystitis is surgery for relief of nasolacrimal duct obstruction called dacryocystorhinostomy (DCR).
Sac massage
Advised for congenital duct obstruction. Done sincerely and regularly in the appropriate manner, more than 90 % of cases resolves.
Probing and Syringing Sac massage
Probing and syringing is generally advised for congenital cases which fail to resolve by sac massaging. The procedure is done under general anaesthesia around one year of age.
DACRYOCYSTORHINOSTOMY (DCR)
What is DCR?
DCR is an operation that treats the infected abscess and the tear duct obstruction simultaneously to improve the drainage of tears from the eye to the nose. It creates a passage between the lacrimal sac and the nasal cavity. The contents of the lacrimal sac are drained directly into the nose.
How is the surgery performed?
A DCR is performed through a skin incision made on the side of the nose. The bone between the tear sac and the nose is removed and the lining of the tear sac is then attached to the lining of the nose to form a permanent drainage for tears to pass from the eyes to the nose.
In some people, during surgery, a clear plastic tube is placed from the inside corner of the eye into the nose. The tube is used to stent the tear drainage system and prevent scarring. This tube is easily removed later.
Sutures are placed in the skin and removed later. The scar produced will initially be red, hard and raised but will smooth out over the months after surgery.
Most patients having DCR surgery can go home on the day of surgery, but a few are kept overnight after the operation.

